
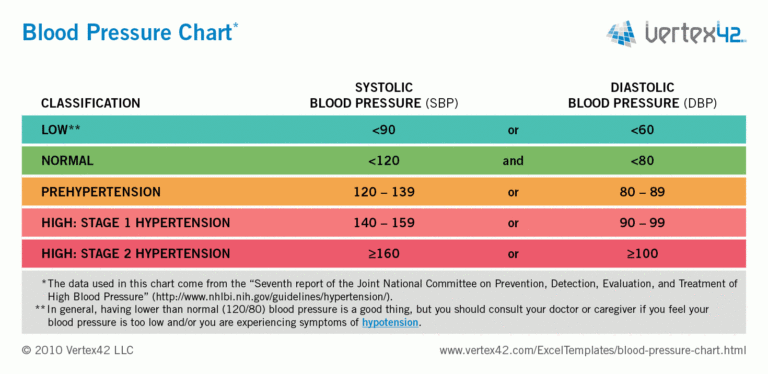
In patients with sepsis, vasopressors are often titrated based on the MAP. There are several clinical situations in which it is especially important to monitor mean arterial pressure. Here are the steps for this calculation:Īnother way to calculate the MAP is to first calculate the pulse pressure (subtract the DBP from the SBP) and divide that by 3, then add the DBP: For example, if a patient’s blood pressure is 83 mm Hg/50 mm Hg, his MAP would be 61 mm Hg. To calculate a mean arterial pressure, double the diastolic blood pressure and add the sum to the systolic blood pressure. Physiology Fundamentals: Mean Arterial Pressure Mean Arterial Pressure Formulas
You may also want to listen to the following podcast. True MAP can only be determined by invasive monitoring and complex calculations however it can also be calculated using a formula of the SBP and the diastolic blood pressure (DBP). It is considered a better indicator of perfusion to vital organs than systolic blood pressure (SBP). MAP, or mean arterial pressure, is defined as the average pressure in a patient’s arteries during one cardiac cycle.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
